Both the 718 alloy and the X-750 alloy belong to the category of precipitation-strengthened superalloys, showcasing impressive attributes like exceptional corrosion resistance, robust strength, and remarkable heat tolerance.
These qualities set them apart from solid solution alloys, a distinction frequently discussed in accessible online articles covering their differences.
Nevertheless, in terms of comparing 718 and X-750 alloys, there’s a scarcity of comprehensive references available.
Within this blog article, we will thoroughly contrast these two alloys by delving into their chemical compositions, applications, and overall performance.
Let’s keep reading.
What is Alloy 718?
718 alloy is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant nickel chromium strip material used at -423° to 1300°F temperature.
The age-hardenable alloy can be readily fabricated, even into complex end finished parts. Its welding characteristics, especially its resistance to postweld cracking, are outstanding.
Products Types of Alloy 718
- Alloy 718 Custom Ring
- Alloy 718 Pipe Spool
- Alloy 718 Custom Flange
- Alloy 718 Round Bar
- Alloy 718 Seamless Pipe
- Alloy 718 Welded Tube
- Alloy 718 Plate
- Alloy 718 Sheet
- Alloy 718 Strip
- Alloy 718 Wire
- Alloy 718 Foil
What is Alloy X-750?
X-750 alloy is a precipitation-hardenable nickel-chromium alloy material used for its corrosion and oxidation resistance and high strength at temperatures to 1300°F.
X-750 alloy, also called UNS N07750 or W. Nr. 2.4669 alloy.
X-750 alloy has excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and fatigue resistance, and it also has good flexibility.
Products Types of Alloy X-750
- Alloy X-750 Custom Ring
- Alloy X-750 Pipe Spool
- Alloy X-750 Custom Flange
- Alloy X-750 Round Bar
- Alloy X-750 Seamless Pipe
- Alloy X-750 Welded Tube
- Alloy X-750 Plate
- Alloy X-750 Sheet
- Alloy X-750 Strip
- Alloy X-750 Wire
- Alloy X-750 Foil
What are the Differences Between Alloy 718 and Alloy X-750?
As you can see from their introduction and products types, alloy 718 and X-750 are very different. Depending on what you are looking for in your project, they each have benefits and drawbacks. For a side by side comparison, you breakdown the differences even further.
Chemical Composition
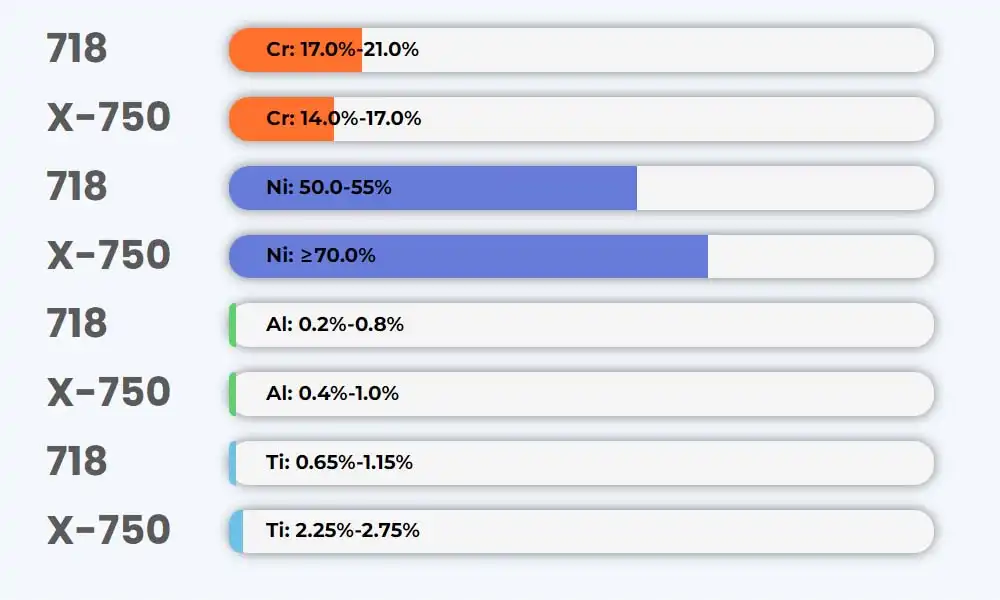
Corrosion Resistance
In comparison to X-750, 718 possesses a higher chromium content.
As a result, 718 exhibits enhanced oxidation resistance when compared to X-750.
Furthermore, Alloy 718 includes molybdenum, a component absent in Alloy X-750. The incorporation of molybdenum serves to enhance the reduction corrosion resistance of 718.
Consequently, 718 outperforms X-750 across all facets of corrosion resistance.
Mechanical Properties
Alloy 718 Mechanical Properties
| Density | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength (0.2%Offset) | Elongation |
| 8.19 g/cm3 | 1260 °C (2300 °F) | MPa – 960 | MPa – 550 | 30 % |
Alloy X-750 Mechanical Properties
| Density | Melting Point | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength (0.2%Offset) | Elongation |
| 8.28 g/cm3 | 1390 °C (2540 °F) | MPa – 910 | MPa – 550 | 25 % |
Applications
Alloy 718 Applications
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Marine
- Oil & Gas Industry
- Petro Processing
- Power & Energy
- Welding Products
Alloy X-750 Applications
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Oil & Gas Industry
- Petro Processing
- Power & Energy
Main Standards
Alloy 718 Products Standards
- Seamless Tube: SAE AMS 5589, SAE AMS 5590
- Bar & Forging: ASTM B637, SAE AMS 5662, SAE AMS 5663, SAE AMS 5664
- Round Bar & Wire: SAE AMS 5962
- Welding Wire: SAE AMS 5832
- Plate & Sheet, Foil & Strip: ASTM B670, ASTM B906, SAE AMS 5596, SAE AMS 5597, SAE AMS 5950
Alloy X-750 Products Standards
- Seamless Tube: SAE AMS 5582
- Bar & Forging: ASTM B637, SAE AMS 5667, SAE AMS 5668, SAE AMS 5669, SAE AMS 5670, SAE AMS 5671, SAE AMS 5747
- Wire: SAE AMS 5698, SAE AMS 5699
- Plate & Sheet, Foil & Strip: SAE AMS 5542, SAE AMS 5598
Cost
While X-750 lags behind 718 in most aspects, the price discrepancy between them isn’t significantly substantial.
This can be attributed to 718’s lower nickel content and elevated iron content. These factors contribute to a reduction in the raw material expenses for the alloy.
Simultaneously, the widespread utilization of 718 results in a substantial supply, thereby lowering its incremental cost.
As a result, if your project is confronted with the decision between these two materials, our suggestion is to prioritize 718. It not only boasts superior performance but also comes at an equivalent cost.
FAQs
What is the density of alloy 718?
Alloy 718 has a density of 8.19 g/cm3, which makes it slightly heavier than other alloys such as copper alloy or aluminium alloy, but lighter than special stainless steel or titanium alloys.
What is the difference between 625 alloy and 718 alloy?
625 possesses considerable amounts of nickel, chromium, and molybdenum making it not only strong at high temperatures but also resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and carburization. One of its most notable characteristics is its ability to prevent stress, pitting and crevice corrosion cracking even when exposed to chloride ions.
718 is an age-hardened version of alloy 625. Aging (or precipitation hardening) produces precipitates in the molecular structure that pins the grains of the metal in place. As a result, materials usually become significantly stronger. In the case of it, 718 has exceptional strength with a yield strength that is about 2x’s stronger than 625.
What is the difference between alloy 718 and 316 stainless steel?
The primary distinctions between 718 and stainless steel 316 lie in their corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength.
In both these aspects, 718 will demonstrate superior performance over the stainless steel 316 alloy.
Why 718 is difficult to machine?
In the production of machined components area, 718 alloy has gained widespread usage, although it’s recognized as a more intricate material to work with.
This complexity stems partially from its elevated strength, resulting in heightened cutting forces exerted at the tool’s tip. Consequently, more robust machinery is necessary to manage these forces effectively.
Yet, the intricacies of machining alloy 718 delve deeper into its ‘metallurgical’ attributes. To begin with, the process of machining induces work-hardening, significantly enhancing the surface strength of the metal.
Due to the relatively low thermal conductivity inherent in nickel-based alloys like 718, there’s a potential for heat accumulation at the tool’s tip during the machining procedure. This accumulation could lead to excessive wear of the tool, thereby diminishing its operational lifespan or necessitating reduced machining speeds.
Does alloy 718 rust?
The high nickel content of alloy 718 makes the alloy have a relatively strong resistance to chloride stress cracking corrosion.
At the same time, due to the presence of chromium, corrosion resistance is even better than pure nickel alloy in the oxidizing environment.
What is the density of alloy X-750?
The density of X-750 is 8.28 g/cm³.
What is the equivalent of X-750?
X-750 equivalent is UNS N07750 and W.Nr. 2.4669.
Are 718 Alloys Better Than X-750 Alloys?
718 excels over X-750 regarding corrosion resistance and strength under high temperatures. Furthermore, 718’s meticulous management of trace elements contributes to its enhanced long-term performance.
In essence, 718 stands as an upgraded iteration of X-750, offering superior performance while maintaining an equivalent cost. Given these factors, it’s a viable initial choice for projects.
Conclusion
In summary, upon a direct comparison of the two metals, distinct disparities emerge, leading us to the conclusion that 718 surpasses X-750 in terms of overall performance. This is primarily due to its higher tensile strength both at room temperature and elevated temperatures.
At Seather, we offer prime quality 718 and X-750 materials and customized products renowned for their exceptional performance. If you require procurement, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with our expert team.






